Do plastic energy chains work for Machine tool applications under hot chips?
Shery George | 28 September 2022
The materials with which igus e-chains are made have to go under a great deal of stress such as pressure and tensile strain, and they are made to be abrasion-resistant, very sturdy and have a high modulus of elasticity, whereby they must also exhibit stable behaviour at high and low temperatures and be resistant to hot chips.
As a rule, the standard temperature range for plastic energy chains is -40°C to +130°C, short-term +170°C. A red-hot chip, however, is considerably hotter, usually above 800°C.
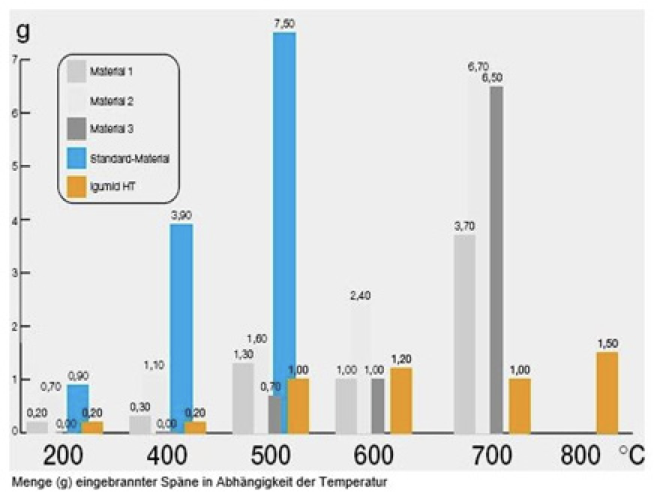
igus uses a special method to treat HT products so that the treated products can withstand short-term temperatures above 850°C. A red-hot chip can therefore no longer fuse with the plastic, as a result of which the e-chain can be used directly in areas where chips occur. In 90% of all cases, it is sufficient if only the lid and floors are made of HT material as they present the largest attack surfaces. Most e-chains and e-tubes can be made of HT material.
p.p1 {margin: 0.0px 0.0px 5.0px 0.0px; font: 12.0px Helvetica; color: #191c1f; background-color: #ffffff}
The amount (g) of chips burned into the material in relation to the temperature

p.p1 {margin: 0.0px 0.0px 5.0px 0.0px; font: 12.0px Helvetica; color: #191c1f; background-color: #ffffff}
Test with liquid aluminium on a “HT energy chain”
